Ultrasound-guided IV insertion training is essential for nurses, enhancing success rates and patient comfort. This technique addresses challenging venous access, improving outcomes in emergency and critical care settings.
Definition and Overview
Ultrasound-guided IV insertion is a medical procedure where nurses use ultrasound technology to visualize veins and guide the placement of intravenous catheters. This technique enhances the traditional landmark-based method by providing real-time imaging, improving accuracy, and reducing complications. Unlike blind insertion, ultrasound guidance allows for precise localization of veins, especially in patients with difficult venous access. The process involves using a handheld ultrasound device to scan the arm or leg, identify suitable veins, and direct the needle into the vein under visual guidance. This method is particularly beneficial in emergency and critical care settings, where timely and successful IV placement is crucial. By integrating ultrasound, nurses can achieve higher success rates and improve patient comfort, making it a valuable skill in modern healthcare.
Importance of Ultrasound Guidance in IV Insertion
Ultrasound guidance significantly enhances the accuracy and safety of IV insertion, particularly in patients with challenging venous anatomy. By providing real-time visualization of veins, it reduces the risk of complications such as nerve damage, hematoma, and missed attempts; This method is especially valuable in emergency and critical care settings, where rapid and reliable venous access is critical. Ultrasound-guided IV insertion also minimizes patient discomfort and anxiety, improving overall satisfaction. Additionally, it decreases the need for central line placements, lowering the risk of associated infections. The use of ultrasound has become a standard of care in many healthcare institutions, as it improves outcomes and streamlines IV placement processes, making it an indispensable skill for nurses.

The Role of Nurses in Ultrasound-Guided IV Insertion
Nurses play a vital role in performing ultrasound-guided IV insertions, ensuring accurate venous access while maintaining patient safety and comfort. Their expertise is crucial for successful outcomes.

Responsibilities of Nurses in Performing the Procedure
Nurses are responsible for assessing patients, identifying suitable veins using ultrasound, and maintaining sterility during insertion. They ensure patient comfort, monitor for complications, and document outcomes accurately. Their role includes using real-time ultrasound imaging to guide catheter placement, reducing the risk of complications like hematoma or nerve injury. Nurses also handle post-procedure care, ensuring proper dressing and patient education. Effective communication with the healthcare team and adherence to infection control protocols are critical. Continuous training and proficiency in ultrasound technology are essential for nurses to perform this procedure safely and efficiently, improving patient outcomes in various clinical settings.
Integration of Ultrasound-Guided IV Insertion into Nursing Practice
Ultrasound-guided IV insertion is increasingly integrated into nursing practice, enhancing patient care and efficiency. Nurses trained in this technique can improve first-attempt success rates, reducing complications and patient discomfort. The integration supports standardized protocols, ensuring consistency across healthcare settings. Institutions encourage nurses to adopt this method through structured training programs and ongoing support. By incorporating ultrasound guidance, nurses can better manage challenging venous access cases, particularly in emergency and critical care environments. This skill not only enhances nursing competence but also elevates the quality of care, making it a valuable addition to nursing practice. Regular updates and competency assessments further ensure its effective and safe application in clinical workflows.

Training Programs for Ultrasound-Guided IV Insertion
Training programs combine didactic instruction, hands-on practice, and simulation-based learning to equip nurses with the skills needed for successful ultrasound-guided IV insertions, ensuring clinical proficiency and patient safety.
Didactic Instruction and Theoretical Foundations
Didactic instruction forms the cornerstone of ultrasound-guided IV insertion training, providing nurses with a solid understanding of anatomy, ultrasound physics, and patient assessment tools. This phase emphasizes theoretical knowledge, such as identifying venous anatomy, understanding Doppler imaging, and interpreting ultrasound images. Nurses learn about validated assessment tools like the A-DIVA scale to identify patients with challenging venous access. The curriculum also covers clinical practice guidelines, infection control protocols, and the principles of sterile technique. Understanding these foundational concepts is crucial for mastering the technical skills required for successful ultrasound-guided IV placement. This theoretical framework ensures nurses are well-prepared to apply their knowledge in real-world clinical settings, enhancing both patient outcomes and procedural efficiency.
Hands-On Practice and Simulation-Based Learning
Hands-on practice and simulation-based learning are critical components of ultrasound-guided IV insertion training. Nurses engage in interactive sessions using phantoms or simulators to practice scanning techniques, vessel identification, and needle guidance. Simulation models mimic real-world scenarios, allowing nurses to refine their skills in a controlled environment. Step-by-step guidance from instructors helps learners master proper hand positioning, probe handling, and catheter placement. Real-time feedback ensures immediate correction of technique. Simulation-based learning enhances muscle memory and confidence, preparing nurses for diverse patient anatomies and challenging cases. This practical training aligns with clinical practice guidelines, bridging the gap between theory and application, and ultimately improving procedural success rates and patient safety.
Step-by-Step Approach to Teaching Ultrasound-Guided IV Placement
A step-by-step approach to teaching ultrasound-guided IV placement ensures systematic skill development. Begin with patient preparation and assessment, followed by ultrasound machine setup and probe selection. Demonstrate vessel identification techniques, emphasizing anatomical landmarks and Doppler imaging. Guide learners through needle insertion, using real-time ultrasound visualization to confirm catheter placement. Reinforce proper hand positioning and ergonomics to minimize fatigue. Incorporate case-based scenarios to address diverse patient conditions, such as difficult venous access. Provide immediate feedback and encourage repetitive practice to enhance proficiency. This structured method ensures learners master both technical and clinical decision-making skills, ultimately improving patient outcomes and procedural success rates.
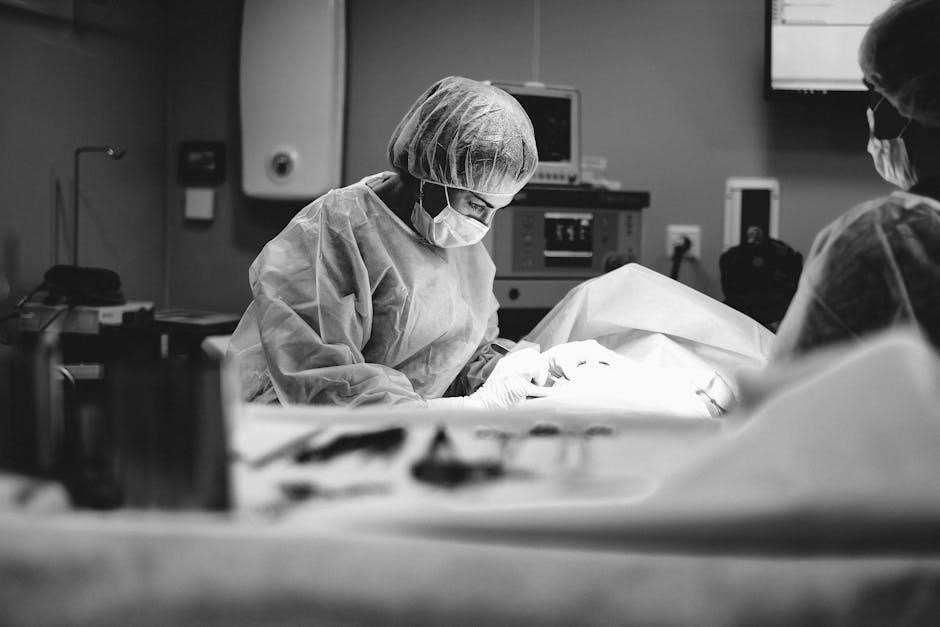
Clinical Applications of Ultrasound-Guided IV Insertion
Ultrasound-guided IV insertion is widely applied in emergency medicine, critical care, and pediatrics, improving venous access in challenging cases and enhancing patient outcomes across diverse clinical settings.
Use in Emergency Medicine
Ultrasound-guided IV insertion is invaluable in emergency medicine, particularly for patients with difficult venous access. It improves first-attempt success rates and reduces complications compared to traditional methods. Emergency departments often use this technique for patients requiring immediate intravenous access, especially in high-stress situations. The ability to visualize veins in real-time enhances accuracy, even in challenging cases such as obese patients or those with edema. Research by Picard (2023) highlights its effectiveness in emergency settings, while Schott (2022) emphasizes its feasibility for nurses. This method minimizes pain and procedural time, making it a preferred choice for urgent care. Its adoption has significantly improved patient outcomes in emergency medicine, ensuring timely and reliable IV access when seconds count.
Application in Critical Care Settings
Ultrasound-guided IV insertion is highly beneficial in critical care settings, where patients often have challenging venous access due to conditions like hypovolemia or edema. This technique allows nurses to quickly and accurately place IVs, even in unstable patients. The real-time visualization of veins reduces the risk of complications, such as infiltrations or nerve injuries, which are particularly concerning in critically ill patients. Research by Gorgone (2022) highlights its effectiveness in improving success rates and minimizing procedural delays. Additionally, ultrasound guidance supports the administration of life-saving medications and fluids in a timely manner, making it an indispensable tool in intensive care units. Its integration into critical care practice has significantly enhanced patient outcomes and streamlined care delivery in high-acuity environments.
Pediatric Considerations for Ultrasound-Guided IV Insertion
Ultrasound-guided IV insertion in pediatric settings requires specialized skills due to smaller vein sizes and deeper tissue depths. Nurses must use lower frequency ultrasound probes for better tissue penetration and adjust techniques to accommodate delicate anatomy. The A-DIVA scale, mentioned in recent studies, helps identify high-risk patients, including children, who benefit from ultrasound guidance. This method reduces multiple needle attempts, minimizing pain and anxiety in pediatric patients. Additionally, the use of topical anesthetics and distraction techniques can enhance comfort. Training programs emphasize child-specific protocols, ensuring nurses are adept at handling the unique challenges of pediatric IV insertion. By mastering these techniques, nurses can improve outcomes and reduce distress in young patients, making the procedure safer and more efficient in pediatric care settings.

Procedural Steps for Ultrasound-Guided IV Insertion
The process involves systematic preparation, ultrasound equipment setup, and patient assessment. Nurses identify veins using ultrasound, guide needle insertion, and monitor placement to ensure accuracy and reduce complications.
Preparation and Patient Assessment
Preparation involves gathering necessary equipment, including ultrasound machines and IV supplies. Patient assessment identifies suitable veins and evaluates medical history for potential complications. Nurses use validated tools like the A-DIVA scale to stratify risk and guide decision-making. Proper positioning ensures optimal vein visibility, while explaining the procedure reduces patient anxiety. Sterility and aseptic techniques are maintained throughout to minimize infection risks. Real-time ultrasound imaging helps visualize venous anatomy, aiding in precise needle placement. This systematic approach ensures safety and effectiveness, particularly for challenging venous access cases.
Ultrasound Technique and Vessel Identification
Ultrasound-guided IV insertion relies on precise imaging to locate and assess veins. Nurses use either the short-axis or long-axis approach, with the short-axis view providing a cross-sectional image of the vein. Vessel identification involves distinguishing veins from arteries by their compressibility and lack of pulsation. Depth and diameter of veins are measured to select appropriate catheters. Real-time imaging guides needle placement, reducing complications. Nurses adjust ultrasound settings, such as depth and gain, to optimize vein visibility. Proper technique ensures accurate placement, minimizing discomfort and improving success rates, especially in patients with difficult venous access. This step is critical for procedural success and patient safety.
Post-Procedure Care and Complication Management
After successful ultrasound-guided IV insertion, proper care is essential to prevent complications. Nurses should secure the IV with sterile dressings and tape to avoid dislodgment. Monitoring for signs of infiltration, phlebitis, or infection is crucial. Patients should be educated on signs of complications, such as redness, swelling, or pain, and instructed to report them promptly. Documentation of the procedure, including catheter type, insertion site, and patient response, is necessary for continuity of care; Regular assessment of the IV site ensures patency and functionality. Complications, though rare, are managed by removing the catheter and addressing issues like infection or thrombosis. Proper post-procedure care enhances patient safety and maintains IV integrity.
Benefits and Limitations of Ultrasound-Guided IV Insertion
Ultrasound-guided IV insertion offers higher success rates and reduced complications, especially in difficult accesses. However, it requires specialized training and equipment, increasing initial costs.
Advantages Over Traditional Landmark-Based IV Insertion
Ultrasound-guided IV insertion offers significant advantages over traditional landmark-based methods. It provides real-time visualization of veins, improving accuracy and reducing complications. This technique minimizes the risk of infiltration, nerve damage, and multiple attempts, enhancing patient comfort. Additionally, it is particularly beneficial in challenging cases, such as pediatric patients or those with difficult venous access. The use of ultrasound also reduces the need for central line placements in some scenarios, lowering infection risks. Overall, ultrasound-guided IV insertion improves success rates, patient satisfaction, and clinical outcomes, making it a valuable skill for nurses in various healthcare settings.
Potential Challenges and Limitations
Despite its benefits, ultrasound-guided IV insertion presents challenges. A significant learning curve exists, requiring nurses to master both ultrasound interpretation and IV placement skills. Equipment costs and maintenance can be prohibitive for some institutions. Additionally, ensuring probe sterility and proper disinfection is crucial to prevent infections. Patient factors, such as obesity or edema, can limit ultrasound visibility, complicating the procedure. Furthermore, reliance on technology may lead to decreased proficiency in traditional landmark-based methods. Finally, the procedure’s success heavily depends on the operator’s skill, emphasizing the need for comprehensive training and ongoing practice to overcome these limitations effectively.

Implementation of Ultrasound-Guided IV Insertion in Clinical Practice
Implementing ultrasound-guided IV insertion requires significant investment in training, equipment, and practice, ensuring nurses master both ultrasound and IV skills to enhance patient outcomes.
Equipment and Technology Requirements
Effective ultrasound-guided IV insertion requires specific equipment, including high-quality ultrasound machines, linear or phased-array probes, and sterile catheters. Portable devices are often preferred for bedside use, while cart-based systems offer advanced features like Doppler imaging. Additional supplies include ultrasound gel, sterile gloves, and appropriate needle guides. The quality of the ultrasound machine and probe significantly impacts image clarity, which is crucial for identifying veins accurately. Proper training on equipment operation is essential to ensure safety and efficiency. Furthermore, institutions must invest in maintaining and updating technology to keep pace with advancements. Challenges such as equipment costs and space constraints can hinder widespread adoption, but the benefits often justify the investment.
Challenges in Adopting the Technique

Adopting ultrasound-guided IV insertion presents several challenges, including the high cost of ultrasound equipment and the need for dedicated space in clinical settings. Training requirements are significant, as nurses must develop proficiency in both ultrasound operation and IV insertion. Availability of experienced instructors and time for hands-on practice can be limiting factors. Additionally, the learning curve for interpreting ultrasound images and coordinating needle placement can be steep for some nurses. Maintenance and updates of ultrasound technology also pose logistical challenges. Despite these obstacles, the benefits of improved success rates and reduced complications make overcoming these challenges worthwhile. Addressing these issues is essential for successful implementation in nursing practice.

Future Directions in Ultrasound-Guided IV Insertion Training
Future advancements include integrating AI, enhancing simulation tools, and expanding training accessibility. These innovations aim to improve proficiency and make ultrasound-guided IV insertion more widely adopted.
Emerging Technologies and Innovations
Emerging technologies in ultrasound-guided IV insertion include AI-driven systems that enhance accuracy and reduce complications. Advanced simulation tools now offer realistic training environments, improving skill acquisition. Handheld ultrasound devices are becoming more portable and user-friendly, enabling faster point-of-care IV placements. Additionally, augmented reality (AR) is being explored to overlay vein anatomy onto patient skin, aiding nurses in real-time. Machine learning algorithms are also being developed to predict vein depth and size, further optimizing the procedure. These innovations aim to make ultrasound-guided IV insertion more accessible, efficient, and reliable, ensuring better patient outcomes and streamlined clinical workflows.
Expanding Training to Other Healthcare Professionals
Expanding ultrasound-guided IV insertion training to other healthcare professionals, such as paramedics and midwives, enhances teamwork and improves patient care. This multi-disciplinary approach ensures that more providers can perform the procedure, reducing delays in emergencies. Training programs are being adapted to suit various skill levels, promoting widespread competency. By involving a broader range of professionals, healthcare systems can optimize resource utilization and improve patient outcomes. This expansion also fosters a culture of collaboration, ensuring that ultrasound-guided IV insertion becomes a standardized skill across healthcare settings. As a result, patients benefit from faster and more reliable venous access, regardless of the provider performing the procedure.